Overview
Cor pulmonale in cattle refers to right ventricular enlargement and eventual failure secondary to pulmonary hypertension, often resulting from chronic lung diseases or hypoxic conditions. This condition leads to systemic venous congestion and is characterized by signs of right-sided heart failure.
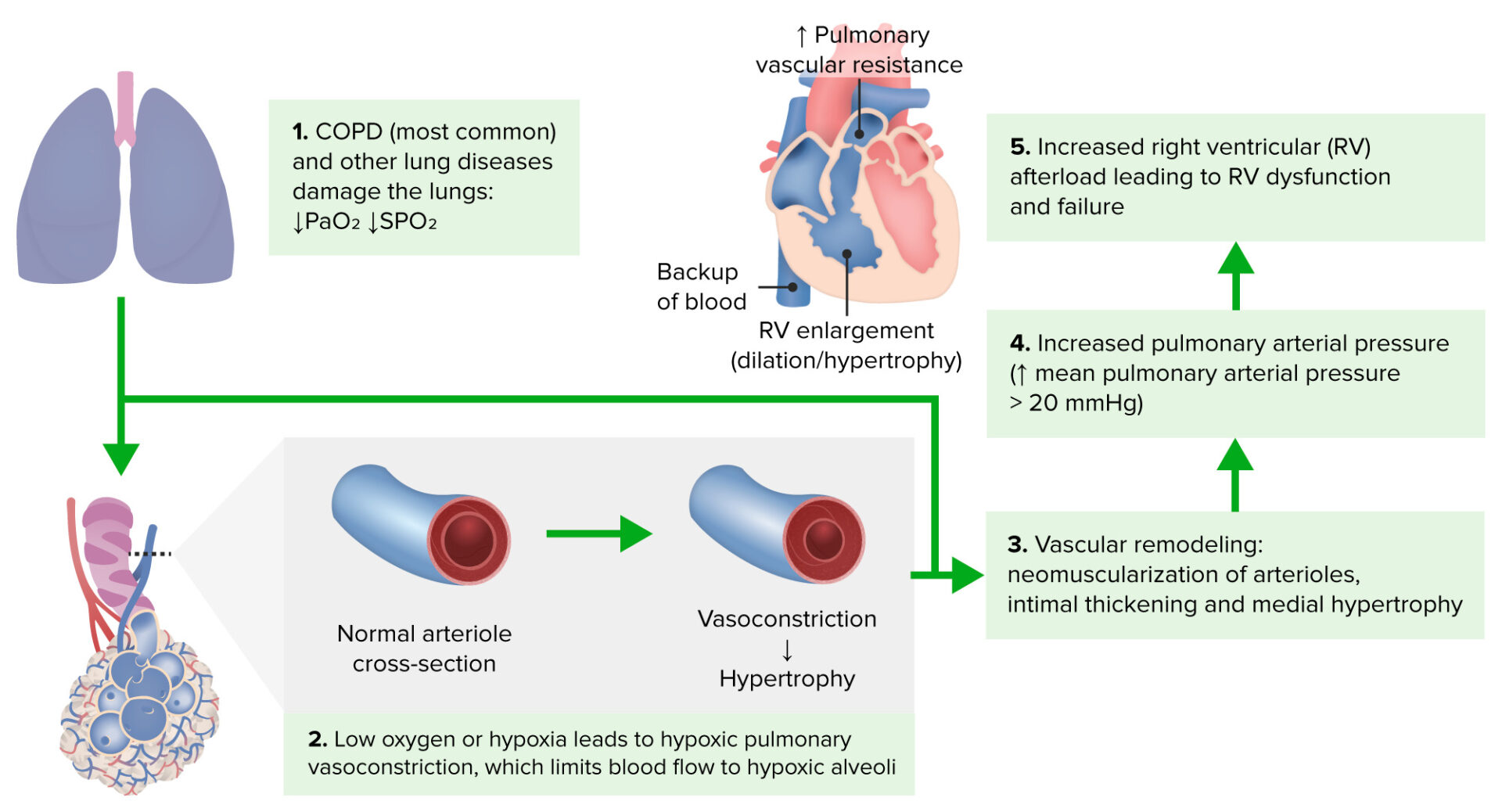
Etiology
- Chronic Lung Diseases: Conditions such as pneumonia, parasitic lung infections, or prolonged exposure to environmental irritants (e.g., dust, ammonia) can lead to pulmonary hypertension.
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Increased resistance in the pulmonary circulation due to lung diseases or high-altitude exposure can elevate pulmonary arterial pressure.
- Other Causes: Congenital heart defects or severe left-sided heart failure can occasionally lead to cor pulmonale.Vin
Clinical Signs
- Respiratory Distress: Difficulty breathing and increased respiratory effort.
- Peripheral Edema: Swelling of the brisket, abdomen, and lower limbs due to fluid accumulation.
- Jugular Vein Distension: Visible pulsation or distension of the jugular veins.
- Lethargy and Anorexia: Decreased appetite and general weakness.PubMed
- Ascites: Fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis
- Clinical Examination: Observation of characteristic signs in cattle with a history of chronic respiratory disease or high-altitude exposure.
- Echocardiography: Assessment of right ventricular hypertrophy and pulmonary hypertension.
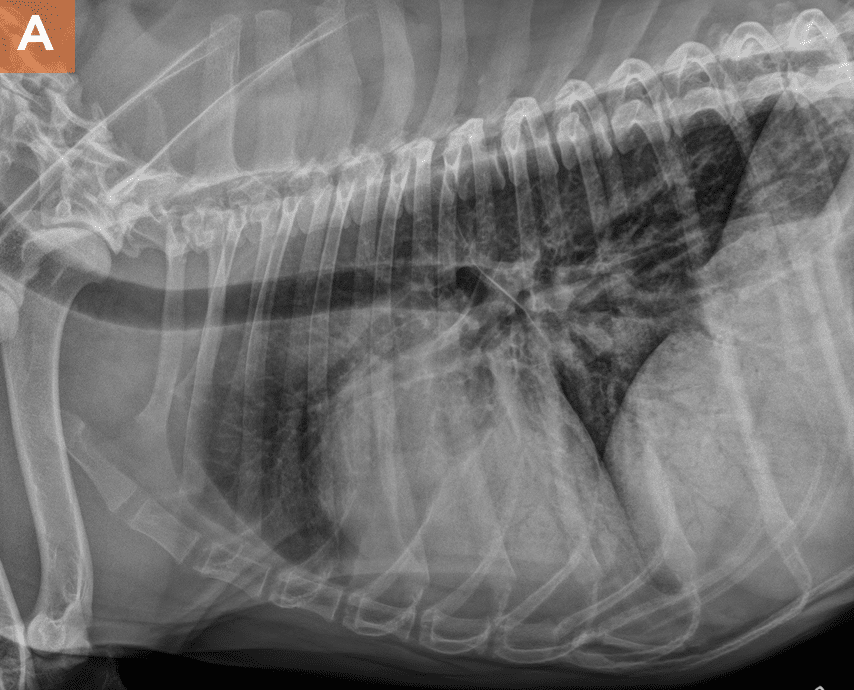
- Chest Radiographs: Evaluation of lung and heart condition; may reveal right-sided cardiomegaly and pulmonary arterial distension.Today’s Veterinary Practice
- Blood Tests: Evaluation of organ function and assessment for underlying diseases.
Treatment and Management
- Addressing Primary Lung Disease: Treatment of the underlying respiratory condition is crucial.
- Diuretics: Administration of furosemide to manage fluid retention and reduce the workload on the heart.
- Bronchodilators and Corticosteroids: To improve lung function and reduce inflammation.
- Oxygen Therapy: In cases of severe respiratory distress.
- Supportive Care: Ensuring proper nutrition and maintaining a stress-free environment.
NAVLE-Style Multiple-Choice Questions
Question 1: Diagnosis
Clinical Scenario:
A 5-year-old beef cow presents with labored breathing, brisket edema, and distended jugular veins. The cow has a history of chronic pneumonia.
Question:
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Left-sided heart failure
B. Pericarditis
C. Cor pulmonale
D. Endocarditis
E. Bovine respiratory syncytial virus infection
Correct Answer: C. Cor pulmonale
Explanation:
The presence of right-sided heart failure signs (brisket edema, jugular vein distension) in a cow with a history of chronic lung disease suggests cor pulmonale, which is right ventricular failure secondary to pulmonary hypertension.
Question 2: Treatment
Clinical Scenario:
A dairy cow diagnosed with cor pulmonale exhibits significant peripheral edema and respiratory distress.Merck Manuals
Question:
Which of the following treatments is most appropriate to manage fluid retention in this cow?
A. Administering furosemide
B. Providing high-sodium diet
C. Using beta-blockers
D. Performing pericardiocentesis
E. Administering penicillin
Correct Answer: A. Administering furosemide
Explanation:
Furosemide, a loop diuretic, is effective in reducing fluid overload associated with right-sided heart failure, thereby alleviating edema and respiratory distress.
Question 3: Differentials
Clinical Scenario:
A cow at high altitude presents with signs of right-sided heart failure.
Question:
Which condition should be considered in the differential diagnosis?
A. Bovine high mountain disease
B. Left-sided heart failure
C. Traumatic reticuloperitonitis
D. Hypocalcemia
E. Mastitis (Merck Veterinary Manual)
Correct Answer: A. Bovine high mountain disease
Explanation:
Bovine high mountain disease is a form of cor pulmonale induced by hypoxia at high altitudes, leading to pulmonary hypertension and right-sided heart failure.
References
- Vetlexicon Bovis. “Congestive heart failure/cor pulmonale in Cows.” Retrieved from https://www.vetlexicon.com/bovis/cardiology/articles/congestive-heart-failurecor-pulmonale/Vetlexicon
- Merck Manual Professional Version. “Cor Pulmonale.” Retrieved from https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/cardiovascular-disorders/heart-failure/cor-pulmonaleMerck Manuals
- PubMed. “Pulmonary hypertension and cardiac insufficiency in three cows with pneumonia.” Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1387897/PubMed
- Today’s Veterinary Practice. “Radiographic Features of Pulmonary Hypertension in Dogs and Cats.” Retrieved from https://todaysveterinarypractice.com/radiology-imaging/radiographic-features-of-pulmonary-hypertension-in-dogs-and-cats/Today’s Veterinary Practice+1Today’s Veterinary Practice+1